Abstract
Introduction: Current recommendations for patients with low-risk polycythemia vera (PV) include hematocrit (Htc) control with phlebotomies and primary prophylaxis of thrombosis with low-dose aspirin. There is scarce information regarding the hematological control, the incidence of complications and the need for cytoreduction in PV patients treated with phlebotomies only.
Methods: A total of 358 patients with low-risk PV (<60 years old and without history of thrombosis) from the Spanish Registry of Polycythemia Vera were included in the present study. PV-related symptoms and blood counts were collected at 6, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 and 60 months from diagnosis while the patients were treated with phlebotomies only. The duration of the treatment with phlebotomies, the indication of starting cytoreduction and the incidence of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic events during the cytoreduction-free period was also analyzed.
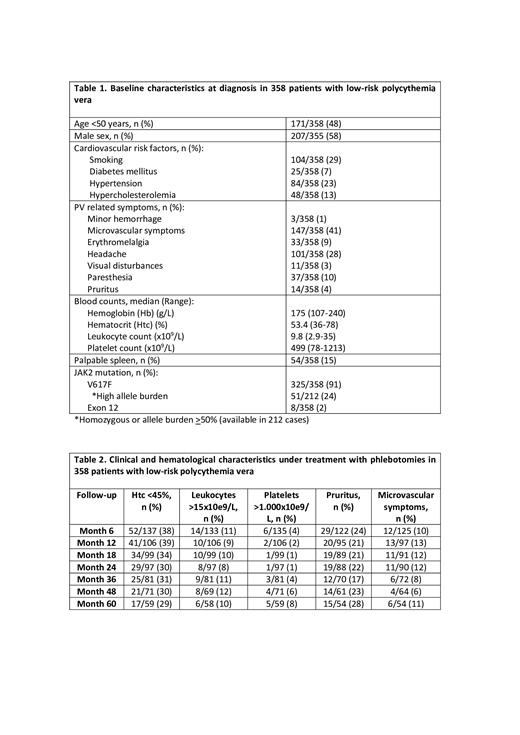
Results: Baseline characteristics at the time of diagnosis are described in Table 1. Table 2 summarizes the main hematological and clinical characteristics under treatment with phlebotomies. Inadequate control of the Htc (> 45%) was reported in 61-70% of the patients, leukocytosis >15x10 9/l in 10% and thrombocytosis >1000x10 9/l in 5%. In addition, about 20% of the patients had pruritus and 10% had microvascular symptoms. Of the 358 patients included, 275 (77%) required cytoreduction, 261 (73%) with hydroxyurea and 14 (4%) with IFN. The main indication of cytoreduction was thrombocytosis (20%), followed by age >60 years old (15%) and microvascular symptoms (13%). Median duration of cytoreduction abstention was 4.7 (0.1-30.4) years being significantly longer in patients younger than 50 years (6 and 2 years for patients younger and older than 50 years, respectively, p<0.0001).
With a follow-up of 1659 person-years under phlebotomy only treatment, 14 thrombosis were observed (arterial n=9, venous n= 5), 12 hemorrhages (major n=4, minor n=8) and 4 solid tumors (1 melanoma and 3 non-cutaneous carcinomas). The incidence of complications during the cytoreduction-free period by person-years was: 0.8% for thrombosis, 0.2% for major hemorrhage and 0.2% for second neoplasia.
The median follow-up until last visit including the time after starting cytoreductive therapy was 8.4 (0.2-39) years. Of 14 deaths observed, none occurred during the phlebotomy period. Half of the patients died from PV related reasons but the other 50% were not related. The median survival estimation by K-M was 36.5 years. Disease progression was documented in 27 (7.5%) patients, 26 of them to myelofibrosis, 1 to myelodysplastic syndrome and none to acute leukemia. Progression to myelofibrosis occurred during the cytoreduction-free period in 5 patients (1.4%) after a median of 5.8 years (Range: 4.9-8.9).
Conclusions The incidence of thrombotic and hemorrhagic complications was very low in this series of low-risk patients treated with phlebotomies, even though only 30-40% of patients maintained the Htc <45%. The data from the present study show that low-risk patients have different therapeutic needs than other PV patients and support the development of new treatment strategies.
Representing the Spanish Group of Myeloproliferative Disorders. GEMFIN
Bellosillo: Qiagen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Thermofisher Scientific: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Ferrer Marin: Cty: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Garcia Gutierrez: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal